Aloe Vera / Ghrita Kumari /ঘৃত কুমারী

General features: It is a shrubby evergreen perennial plant belonging to Liliaceae family of Aloe genus. The plant grows in hot and dry climate. It has been first identified in the Arabian Peninsula. About 250 or more species and a large section of subspecies are hitherto categorized botanically. Among them Aloe Vera is the important one for human use that has been noticed over a long period of time. The plant, Aloe Vera carries several different names also eg, Aloe barbadensis Mill, Aloe chinesis Bak, Aloe elongate Murray, Aloe indica Royale, Aloe Officinalis Forsk etc. In Sanskrit as well as in Bengali it is named as Ghrita Kumari (ঘৃত কুমারী), meaning a delicate virgin. As per the folk medicinal use, it is commonly believed that it has the rejuvenating power to bring back the bubbly youth within female, not just by providing only good skin but also curing the problems associated with menorrhea and others. From the time of ancient Rigveda (1500 – 1800 BC) the plant has been designated as being the sources of vigor offering sound health offering utmost vibrancy. By appearance, it is a spiky cactus xerophytes (grown with less water) with fleshy succulent leaves that grows in a decorative pattern possessing short stems. Usually, a matured plant expresses 20 – 30 leaves. Each stem grows up ~ 1 – 2 ft high displaying bright green color. The inflorescence is a dense raceme borne on a peduncle of ~ 1 ft high. The flowers are yellow – orange with pendant appearance. The flower stems grow ~ 2 ft in height. The plant reaches to the maturity in ~ 4 years that can last up to ~ 12 years while holding the ground tightly with thick fibrous roots. The small fruits are triangular and capsule like shape having numerous seeds inside. In recent days, it is cultivated for the medicinal and cosmetic purposes. It also finds uses in various beverages, ointments or lotions particularly applicable toward the burn victims. The plant is widely appreciated all over the world including far Eastern countries for the sake of its role in skin care which has been observed from a very ancient time, ~ 6000 BC. The use of Aloe is already mentioned in the millennial old Egyptian and Mesopotamian literatures especially for the skin care and laxative needs. Evidences further indicate that the plant has the capability of lowering LDL and blood glucose with simultaneous enhancement of HDL level. It can be used topically in treating the genital herpes and psoriasis. Recently, it is claimed that the plant extract can control HIV / AIDS infection. Its beneficial effects are also observed regarding rapid healing of burns, suppressing allergies while boosting the immune system, or curing any damages due to frost bite, preventing cancer in lung and preventing intestinal disorders. The central part of the leaves has thin walls holding colorless mucilaginous jelly popularly called Aloe gel. It possesses water (99 %), glucomannans, lipids, amino acids, sterols and few vitamins. Whereas underneath the skin of middle layer holds Aloe juice. It contains several chemicals of bitter taste providing powerful laxative property due to the anthraquinone content. The outer thick layer known as rind offers protective function to plant which is composed of carbohydrates and proteins involved in the transport of water, solutes and starch.
Common home uses: As a folk medicine it is still used in the home remedy for following reasons.
- Skin care
- Wound healing
- Treatment for diabetes
- Anti-inflammatory reasons
- Immunomodulatory role
- Anti-cancer effect
- Treating burns.
History of Aloe use: Countless fascinating tales exist about Aloe particularly regarding its use that can be traced back to few millennia even before the appearance of Christ. The records show that Aloe juice was commonly practiced by the women for skin care in the ancient Egypt around 6000 BC. It was defined as a sacred plant therefore as per the popular belief spread, its ‘blood’ (juice) enables to unveil the secrets of beauty, health and immortality. The legendary beauty of Cleopatra and Nefertiti has been claimed to be derived from the daily use of skin nourishing juice of Aloe Vera. Additionally, in ancient Egypt, even the dead were embalmed by using the Aloe juice for its antibacterial and anti-fungal properties. The Egyptians used to believe strongly that by preventing the decomposition of cadavers, dead can earn the eternal life. They defined Aloe Vera as being the ‘plant of eternity’. Its anti-inflammatory effect was first documented in the ‘Papyrus Eber’ (Ancient Egyptian medical practice journal documenting the use of various herbs written on the Papyri) ~ 1550 BC. The written record of Aloe Vera use on a clay board was first appeared in the oldest Sumerian city, Nippur of Mesopotamia (recent day Iraq) around 2200 BC. At that time, it was a folk belief that any illness is an act of devil capturing the human body. So Aloe being a divine plant possesses the power to exorcise that demonic action. The use of Aloe for healing wounds during wars was routinely performed by the soldiers of Alexander the Great (350 – 320 BC). It is for which Aristotle once convinced Alexander to capture the island, Socotra (Archipelago in the Arabian Sea under recent Yemen) that had the large groves of Aloe which would satisfy the medical needs of the wounded warriors. Afterward around ~ 50 BC, following the Egyptians and Romans, its use turned intensely popular. The famous Greek naturalist Dioscorides mentioned Aloe Vera highly in his teaching books on pharmaceutics and plant therapy, which he compiled during his extensive travel in the orient. Aloe was his favorite healing plant. He prescribed its juice for numerous physical problems like, treatment of wounds, intestinal discomfort, skin irritation, gingivitis, sunburn, acne, hair loss and arthralgia. Its use in Chinese medicine was recorded by Marco Polo. In ancient Japan, it was known as “Royal plant” and its juice was consumed by the Samurai for maintaining good health. The use of Aloe Vera has been broadly described in “Rigveda” of ancient India in the name of “Ghrita Kumari” for its beneficial role on health particularly for maintaining acne free moist and glazy skin. Aloe was also quite familiar within native Indian tribes of North America according to the 16th century record. Natives used to apply its juice particularly on skin for repelling the insects. They also consider it as a holy plant for its numerous beneficial effects on health. The European history indicates that Columbus was carrying Aloe Vera growing in pots onboard his armada during the expedition. The expedition helped spread its use. In 16th century, Jesuit monks trained people for the use and also helped widening its cultivations for the sake of healing wounds. The Maya Indians in southern hemisphere of American continent labeled the plant juice as a “Fountain of Youth” for its invigorating role on health and beauty. In modern days, it is used for both medicinal and cosmetic needs.
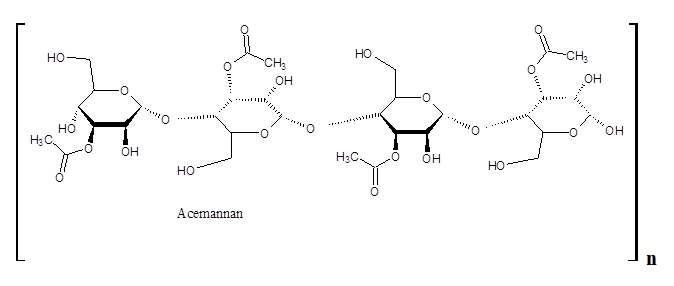
Importance of Aloe Vera gel: The gel is widely famed for its beneficial role to control various ailments due to numerous chemical contents. The major active agents identified are anthraquinone derivatives and polysaccharides. Usually, the anthraquinones are famously known for their laxative actions. Among the polysaccharides, the notable one is Acemannan. It is a large (Mw ~ 1700) hydrophilic mucopolysaccharide connected via the β – 1- 4 glycosylated linkage having D – mannoacetate monomer. The compound has immunostimulant, antiviral, antineoplastic and gastrointestinal role.
The combined action of those ingredients within gel promotes the healing of numerous wounds. Besides healing wounds, it also has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral, Gastroprotective, antifungal, antioxidant, antioxidant, laxative, immune stimulant and hypoglycemic role. The recent clinical evidences show that Aloe gel quickens the healing of versatile wounds, from burn to frostbite. It also lowers LDL while enhancing the HDL level in blood. Additionally, it reduces the blood glucose level, prevents / cure genital herpes, psoriasis, papilloma virus, seborrheic dermatitis, xeroderma, mouth ulcers and lichen planus. Besides its topical applications on skin the oral ingestion is frequently allowed preventing or curing various health problems.
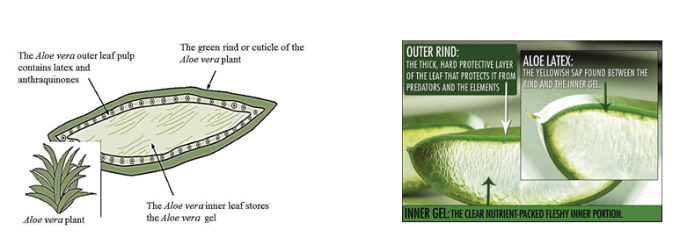
Chemical contents: The different sections of plant is loaded with numerous chemical components. Varieties of medicinal products and cosmetics are prepared using the gel collected from the inner part of leaf. The outer leaf pulp (see the picture) produces yellow latex which is extremely bitter in taste due to the existence of anthraquinone like compounds, Aloin, Aloe-emodin and others. This part of the leaf produces strong laxative effect due these compounds.
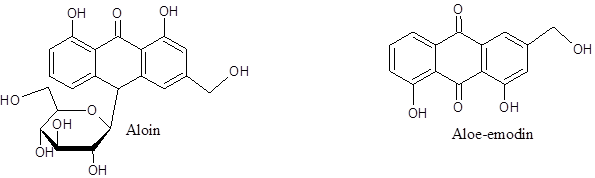
Aloin exerts intestinal contractions by enhancing peristalasis especially in colon inducing severe bowel movements. The compound opens up Cl– ion channels situated on the colonic membrane preventing water reabsorption of colon within the gastro-intestinal tract that essentially makes the stool softer. The combined effects of contraction and prevention of water reabsorption provides strong laxative effect. It also causes uterine contractions so any products of Aloe vera should be avoided by pregnant women. Similar role is noticed for Aloe-emodin. But Aloe-emodin also has strong anti-viral effect particularly against Herpes simplex virus 1 & 2.
The inner core pulp has various ingredients, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, amino acids, vitamins, enzymes, small organic compounds and inorganic minerals. Considering the overall weight, the water content of fresh pulp is ~ 99.5 % whereas the rest, 0.5 % consists of solid ingredients. As per dry weight concern, polysaccharides ~ 55 %, sugars ~ 17 %, minerals ~ 16 %, proteins ~ 7 %, lipids ~ 4 % and phenolic components ~ 1 %. Often the seasonal variations are noticed in those levels. Table below shows the different chemical ingredients in the leaf.
| Components | Composition |
| Water (~ 99.5 %) | |
| Sugars | Monosaccharides – Glucose, Fructose, Mannose, L- rhamnose,
Aldo-pentose. Polysaccharides – Glucomannans |
| Anthraquinones | ~ 12 anthraquinones exist. Important ones are: Aloin, Aloin-emodin,
Isobarbaloin, Anthranol, Emodin, Ester of cinnamic acid, Chrysophanic acid, Aloetic acid and Resistanol. |
| Proteins | ~ 0.07 %. Lectins and lectin like substances.
|
| Enzymes | Cellulase, Aliiase, Peroxidase, Alkaline phosphatase, Amylase,
Carboxypeptidase, Catalase, Cyclooxidase, Cyclooxygenase, Lipase, Superoxide-dismutase, Bradykinase. |
| Vitamins | A, C, E, B1, B2, B6, B12, Niacin, β – carotene, Choline & folic acid.
|
| Steroids | 4 plant steroids. Campesterol, Lupeol, Sistosterol & Cholesterol. |
| Essential oil | Tridecanoic acid, Phytol, Oleic acid, 1-octanol, Squalene,
Butyl-heptadecyl ester, 9,12,15,-octadecatrienoic acid ester, Allyl- Pentadecyl ester, Eicoane, 9-octadecenal, Di-dodecyl pthalate, Hexyl Pentadecyl ester, α – tocopherol and some others. |
| Organic fatty acids | N – hexadecanoic acid, Oxalic acid, 9,12-octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z),
Arachidonic acid, γ – linoleic acid, Gibberlin, Malic acid, Lactic acid, Succinic acid, Salicylic acid, Uric acid etc. |
| Minerals | 10 – 25 % of the dry matter. K, Na, Cl, Ca, Mg, P. Trace elements
Cu, Fe, Zn, Mn, Al, Se, Cr, Pb, Co, Ba. |
| Plant hormones | Auxins and Gibberelin. |
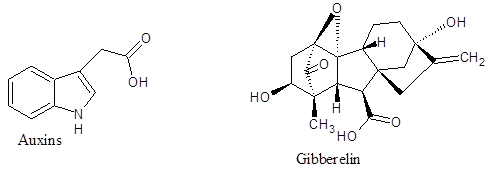
Auxins and Gibberelin are the plant hormones. Auxin is highly needed for the sake of cell growth and its differentiation. It is responsible for the expression of a bunch of important genes while helping their transcription. In that way, Auxins decides the arrangement or configuration and also development of a plant. Gibberelin controls the growth and other developmental processes that includes elongation of stems, germination, flowering and induction of various enzymes within plant cells.
Significant pharmacological roles: Several common pharmacological actions have been cited which are already clinically proven.
Anti-inflammatory effect – In general inflammation is caused by an injury. As per the etiology, it is a collection of biological reactions expressed as swelling, edema, pain, heat, redness often leading to loss of functionality. Sepsis on the other hand is a life threatening event caused by unrestrained activation of inflammatory pathway imposing multiple organ failure leading to the fatality. In all cases, the use of Aloe Vera improves the situation. It inhibits leucocyte cell adhesion subsequently the generation of inflammatory cytokines (TNF – α, IL – 1b and IL – 6), PGE2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and COX-2 mRNA expression. The gel blocks the Arachidonic acid pathway to produce PGE2. The responsible compounds are identified to be Aloin and Aloe-emodin.
Anti-cancer effect – The Aloe extract shows positive effect in treating the cancers. Aloe gel exerts chemopreventive and anti-genotoxic effects on Benzo[α]pyrene-DNA adducts. In addition, lectins and polysaccharides particularly, Acemannan shows reduction of tumor burden, shrinkage and necrosis consequently prolonging the survival rates among the animals. The stimulation of immune system has been identified to be the major cause. Some also verifies that disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential, release of cytochrome C and activation of Caspase 3 by the Aloe – emodin could be the underlying factor behind this anti-tumor effect.
Effect on burn and wound healing – The rapid rate of wound healing by Aloe gel is a noteworthy fact which is known for a very long time. It is seen to be effective even in the case of second degree burns which has been verified by numerous animal experiments. The major contributory factor identified is Acemannan, β – (1, 4)-acetylated polymannose. The compound stimulates the expression of VEGF and other related factors like Keratinocyte growth factor -1 and simultaneously levitates the production of type – 1 Collagen. It is particularly beneficial for the oral wound. Besides Acemannan, Aloe extract also possesses multiple pro-angiogenic components. The notable one is β – sitosterol which enhances the expression of various proteins and growth factors (VEGF, VEGF receptor Flk-1, blood vessel matrix laminin & von Wilde Brand factor) helping increase the progression of angiogenesis. The reports from various animal research further has convinced that partial thickness burns treated with Aloe gel heals faster that the silver -sulfadiazine.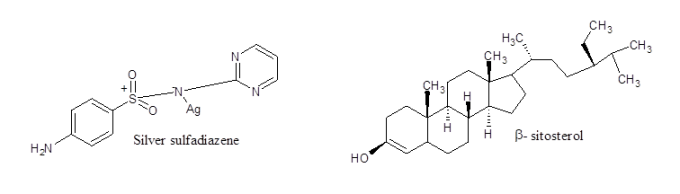
It has been observed that delaying of wound healing is a crucial problem for patients underwent radiation treatment or subjected to any irradiation. Clinical studies showed that Aloe Vera can expedite the healing process in this situation. The treatment with Aloe significantly increases the production of several growth factors like bFGF and TGF-β-1.
Anti-diabetic effect – Multitude of evidences indicate that oral consumption of Aloe juice reduces the fasting glucose level and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c). Some further claim that Aloe also lowers the LDL, total cholesterol and triglyceride. Experiments indicate that antioxidant effect of polyphenolics, flavonoids, vitamin C and E is majorly liable behind this event. Additionally, Aloe juice contains significant amount of Cr, Mn and Zn which together potentiate the antidiabetic effect. Cr particularly enhances the insulin binding leading to the increased uptake of glucose into cells. It also improves glucose tolerance and decreases the fasting blood glucose level.
Miscellaneous beneficial effects – A few of them are transcribed below:
- Microbial effect – The juice shows several microbial effects.
- Helping vitamin C & E absorption in the body.
- Enhancing Insulin transport across the cell membrane.
- Enhancing the absorption of several drugs which show poor bioavailability. Example is fluoxetine, anti-depressant drug.
Adverse effects: A few adverse actions of Aloe have been noted which are related to allergic manifestations like dermatitis in case of sensitive individuals. The actions are possibly due to anthraquinone derivatives like Aloin or Barbaloin. But the existence of Aloesin in Aloe gel which is often used as skin whitening agent might cause some unpleasant actions.
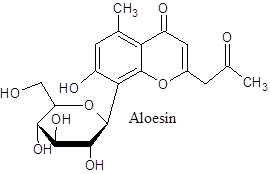
Aloesin blocks melanogenesis inhibiting Tyrosinase blocking hydroxylation of tyrosine to 3, 4 -dihydroxy phenyl alanine (DOPA) and oxidation of DOPA to Dopaquinone. In that context, the oral use of Aloe should be carefully considered. Although no toxic activity has been reported so far. Further the laxative actions might lower the Potassium level. All actions are reversible. But the use of Aloe during pregnancy should be avoided.
