Demystifying the world of nutritional science, this piece focuses on polyunsaturated fats – their essence, their role, and the benefits they deliver to your body. These nutrients are pivotal players in your overall health, participating in various physiological functions and activities. Understanding their significance can reshape your dietary choices and pave the way towards a healthier lifestyle.
This examination of polyunsaturated fats not only elucidates their definition but also elaborates on their diverse types and the sources from which they can be derived. From highlighting their importance to outlining the potential health benefits and risks they carry, the intention is to provide comprehensive and easily digestible information.
What is Polyunsaturated Fat?
When the term ‘polyunsaturated fat’ is brought into conversation, what does it denote? In essence, it refers to a type of dietary fat (unsaturated fat) that contains more than one double bond in its chemical structure. These double bonds induce a ‘kink’ in the molecule, preventing it from packing tightly and thereby rendering it liquid at room temperature.

These polyunsaturated are predominantly found in plant-based oils and certain types of fish. Not only are they a vital energy source, but they also contribute to cell function and the upkeep of your body’s core temperature. They play a cardinal role in synthesizing hormones that control inflammation and blood clotting, among other vital tasks.
What is the other term for Polyunsaturated Fat?
Another term frequently associated with polyunsaturated fat is ‘polyunsaturated fatty acids’. It’s a more technical name for the same substance, highlighting its chemical composition. These fats are often deemed ‘healthy fats’, setting them apart from their less desirable counterparts (saturated and trans fats). This designation underscores their pivotal role in maintaining health, especially heart health.
What is the characteristic of Polyunsaturated Fat?
Polyunsaturated fats are unique due to their chemical structure. With multiple double bonds, they differ significantly from saturated fats, which contain only single bonds. This structural peculiarity grants them fluidity at room temperature, unlike saturated fats that remain solid.
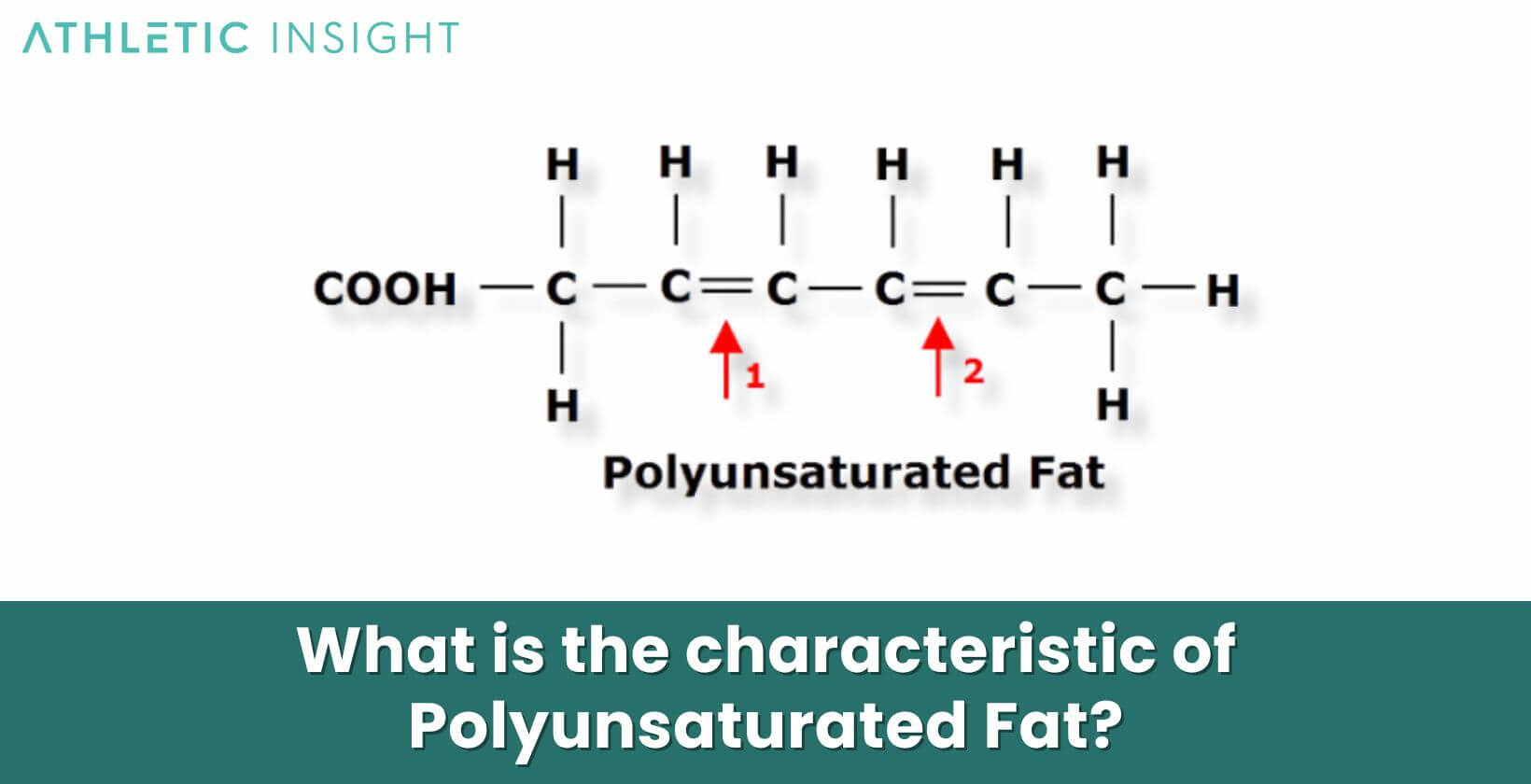
Polyunsaturated fats play a pivotal role in supporting bodily functions. They contribute to cell membrane structure, hormone production, and anti-inflammatory processes. However, one notable trait of these fats is their inability to be produced by the human body. So, it becomes critical to obtain them through our diets.
What is the importance of Polyunsaturated Fat?
The importance of polyunsaturated fats can’t be overstated. Essential for many bodily functions, they assist in the synthesis of certain hormones and are an integral part of cell membranes. This facilitates communication between cells, promoting optimal function throughout the body.
Polyunsaturated fats play a significant role in maintaining heart health. They can help reduce levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), or ‘bad’ cholesterol, while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL), or ‘good’ cholesterol. The positive impact on cholesterol levels subsequently reduces the risk of heart disease, emphasizing the vital nature of these fats.
Why are Polyunsaturated Fats better than Saturated Fats?
The contrast between polyunsaturated and saturated fats is stark. While both are types of dietary fat, their impacts on health diverge significantly. Saturated fats, often found in animal products and tropical oils, can increase LDL cholesterol levels when consumed in excess, enhancing the risk of heart disease.
Polyunsaturated fats can also improve heart health by positively modulating cholesterol levels. By incorporating polyunsaturated fats into your diet, you can counterbalance the negative effects of saturated fats.
What are the classes of Polyunsaturated Fats?
Polyunsaturated fats are subdivided into different classes based on their chemical structure and function. The two main types are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Less common, yet still important, is the omega-9 class. Each of these has unique roles within the body, supporting various aspects of your health.
While each class of polyunsaturated fats contributes to overall wellbeing, they differ in their food sources and specific health benefits. For example, omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health, while omega-6 fatty acids support skin and hair growth.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Omega-6 Fatty Acids
- Omega-9 Fatty Acids
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
The omega-3 class of polyunsaturated fats holds a special place in the world of nutrition. Comprising three primary types—ALA, EPA, and DHA—these fatty acids are essential for your health, and are chiefly found in fatty fish, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in brain function, as well as normal growth and development. They may also contribute to reducing inflammation, which is crucial for preventing chronic diseases such as heart disease and arthritis. The human body cannot produce these important fats, emphasizing the need to include omega-3 rich foods in your diet.
2. Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-6 fatty acids, another essential class of polyunsaturated fats, include linoleic acid (LA) and arachidonic acid (AA). Mainly found in vegetable oils, nuts, and seeds, they are vital for normal growth, brain function, and skin and hair growth.
Just like omega-3 fats, the human body cannot produce omega-6 fats, making them an essential part of our diet. Though they play many positive roles in the body, it’s crucial to maintain a balance between omega-6 and omega-3 intake, as an excess of omega-6 can lead to inflammation.
3. Omega-9 Fatty Acids
Last on the list is omega-9 fatty acids, an intriguing member of the polyunsaturated fat family. The primary omega-9 is oleic acid, predominantly found in canola oil, sunflower oil, and other plant-based sources.
Unlike omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, omega-9 fatty acids are not classified as essential fats. This means that although they have numerous health benefits, our bodies can produce them if they are not available in our diet. They can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke by promoting healthy responses to inflammation and enhancing immune function.
How do people incorporate Polyunsaturated Fats into their Diets?
Incorporating polyunsaturated fats into the diet is simple. Start by replacing foods high in saturated fats, like red meat and full-fat dairy products, with foods high in polyunsaturated fats. Now, opt for fish such as salmon or mackerel, choose oils like sunflower or canola for cooking, and snack on a handful of walnuts or sunflower seeds.
Consider also including fortified foods in your meal plan. Many products such as eggs, yogurt, and milk are fortified with omega-3s. You may also want to try tofu or tempeh, both excellent plant-based sources of polyunsaturated fats. Diversifying your diet this way will help ensure you consume a healthy balance of fats.
What type of Diet is perfect for Polyunsaturated Fats?
A diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low in saturated and trans fats is ideal for maximizing the benefits of polyunsaturated fats. This kind of diet is epitomized by the Mediterranean diet, which is rich in fish, nuts, seeds, and plant oils—all excellent sources of polyunsaturated fats.
Still, it is not just about which foods you eat, but also the proportion. The American Heart Association recommends that 25% to 35% of your daily calories come from fats, with the majority being unsaturated fats, including polyunsaturated fats. This balance helps ensure optimal nutrient intake without contributing to weight gain or heart disease.
Does Polyunsaturated Fat affect weight loss?
Yes, the relationship between polyunsaturated fats and weight loss is highly related to one another. While fats are high in calories, with 9 calories per gram compared to 4 for proteins and carbohydrates, they are not inherently fattening. In fact, including the right types of fats, like polyunsaturated fats, in your diet can contribute to weight loss.
Research indicates that polyunsaturated fats may help reduce body fat. This is likely because these fats help you feel satisfied after meals, preventing overeating. They also play a role in regulating metabolism. So, while it’s crucial to monitor your overall calorie intake for weight loss, don’t shy away from these healthy fats.
What are the food sources of Polyunsaturated Fats?
Locating polyunsaturated fats in your local grocery store is simple. Many common foods are excellent sources of these beneficial fats. The most potent sources include certain types of fish, seeds, nuts, and plant-based oils. Lesser known but still valuable sources include fortified foods and certain types of vegetables.
By understanding where to find these fats, you can easily incorporate them into your meals. A diet rich in polyunsaturated fats can contribute to improved heart health, better brain function, and a range of other health benefits.
- Fatty Fish
- Fortified Foods
- Nuts and Seeds
- Nut Butter
- Plant-based Oils
- Soybeans and Tofu
- Fish Oil and Algal Oil Supplements
1. Fatty Fish
Fatty fish are a powerhouse of polyunsaturated fats, specifically omega-3 fatty acids. Species such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are brimming with these beneficial fats. Not only do they contribute to heart and brain health, but they are also an excellent source of high-quality protein.
For example, a 3.5-ounce serving of salmon contains roughly 4 grams of omega-3 fatty acids. Given the substantial health benefits associated with these fats, consider adding a serving or two of fatty fish to your diet each week. Whether you prefer them grilled, baked, or in a salad, fatty fish can elevate your meals to a new level of healthfulness.
2. Fortified Foods
Fortified foods are products to which extra nutrients have been added. Some manufacturers enrich their products with omega-3 fatty acids, providing another way to boost your intake of polyunsaturated fats. Examples include certain brands of eggs, milk, yogurt, and bread.
As an example, omega-3 enriched eggs are produced by feeding hens a diet high in flaxseed, a rich source of omega-3. Consuming these fortified eggs can contribute to your overall intake of polyunsaturated fats. When shopping, always check the packaging to ensure you’re choosing omega-3 enriched products.
3. Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are another excellent source of polyunsaturated fats. Walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds are particularly rich in these healthy fats, especially omega-3 fatty acids. Moreover, they are packed with other beneficial nutrients like fiber and protein.
For example, just one ounce of flaxseeds provides about 6.5 grams of polyunsaturated fats. As versatile ingredients, nuts and seeds can be easily incorporated into your diet. Enjoy them as a snack, add them to smoothies or salads, or use them in baking to add a nutritious crunch to your meals.
4. Nut Butter
Nut butter, such as almond or peanut butter, is another way to get your polyunsaturated fats. These spreads are packed with both nutrition and flavor, making them a favorite among children and adults alike. As with whole nuts and seeds, they contain a healthy dose of polyunsaturated fats along with other beneficial nutrients.
For example, a two-tablespoon serving of almond butter contains around 5 grams of polyunsaturated fats. It’s an easy addition to your breakfast toast, smoothies, or used as a dip for fruits and vegetables. Just make sure to choose varieties without added sugars or oils to keep your nut butter as healthy as possible.
5. Plant-based Oils
Plant-based oils, especially those derived from seeds, are a rich source of polyunsaturated fats. Canola oil, sunflower oil, soybean oil, and flaxseed oil are all loaded with these healthy fats. They can be used in cooking or as a dressing for salads, adding a dose of heart-healthy fats to your meals.
As an illustration, one tablespoon of sunflower oil contains about 8.9 grams of polyunsaturated fats. This contributes to its light, pleasant flavor, and high smoke point, making it a versatile oil suitable for various cooking methods. Remember, as with all oils, it’s important to use them in moderation due to their high calorie content.
6. Soybeans and Tofu
Soybeans and soy products like tofu are an outstanding source of polyunsaturated fats. These plant-based proteins are not only nutritious but also versatile, making them a favorite among vegetarians and vegans.
A half-cup serving of tofu, for instance, offers about 5.5 grams of polyunsaturated fats. Its mild flavor and firm texture make tofu a great addition to a variety of dishes, from stir-fries to smoothies. Whether you’re a tofu aficionado or a curious newbie, incorporating this soy product into your diet can be a great way to boost your intake of polyunsaturated fats.
7. Fish Oil and Algal Oil Supplements
If you’re not a fan of fish or are looking for a convenient way to increase your omega-3 intake, fish oil and algal oil supplements can be a practical option. They are concentrated sources of omega-3 fatty acids, making them a popular choice for those seeking the health benefits of these polyunsaturated fats.
It’s crucial, however, to choose high-quality supplements and to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen. This ensures that you’re selecting a product that’s safe, effective, and aligns with your overall health goals.
Is an Avocado a Polyunsaturated Fat?
No, avocado is not high in polyunsaturated fat. The nutritional composition of avocados is unique. While they are indeed a source of fat, the majority is monounsaturated fat. These fats are also beneficial for heart health, similar to polyunsaturated fats. Still, avocados do contain some polyunsaturated fats.
In a one-cup serving of avocado, you’ll find approximately 2.7 grams of polyunsaturated fats. While they are not the richest source of these particular fats, their overall nutrient profile makes them a valuable addition to a balanced diet. So, continue to enjoy your avocado toast, knowing it’s part of a heart-healthy eating pattern.
Are eggs high in Polyunsaturated Fats?
No, although eggs contain a variety of fats, they are not a primary source of polyunsaturated fats. The fat content in eggs is predominantly made up of monounsaturated and saturated fats. However, they do contain a smaller amount of polyunsaturated fats.
Specifically, one large egg contains approximately 1.4 grams of polyunsaturated fats. Remember, eggs are also packed with other vital nutrients, including high-quality protein and essential vitamins and minerals, making them a wholesome food choice in moderation.
What is the recommended daily intake of Polyunsaturated Fats?
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend that adults get 20% to 35% of their daily calories from fats, with a focus on consuming polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats. Considering that fats provide 9 calories per gram, this equates to approximately 44 to 77 grams of total fat for a 2,000 calorie diet, with an emphasis on polyunsaturated fats.
It’s worth noting that there are specific recommendations for omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Adults should aim for about 1.6 grams of omega-3 fatty acids and 14 grams of omega-6 fatty acids per day. Keep in mind that these recommendations can vary based on factors such as age, gender, and overall health status.
What are the health benefits of Polyunsaturated Fats?
Research suggests that polyunsaturated fats, particularly omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, play a significant role in overall health. First, these fats contribute to heart health by helping to lower levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol while increasing “good” HDL cholesterol. As a result, they may reduce the risk of heart disease.
Polyunsaturated fats also support brain health. Essential fatty acids, such as DHA, are crucial for cognitive function and neurological development. Omega-3 fats also exhibit anti-inflammatory properties and could potentially aid in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. It’s important to remember that these benefits are best achieved through a balanced diet that incorporates a variety of food sources of these vital fats.
- Improved heart health
- Support brain health
- Exhibit anti-inflammatory properties
What are the health risks of Polyunsaturated Fats?
While polyunsaturated fats have several health benefits, they should still be consumed in moderation. Like all types of fat, they are high in calories, which could contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess. Too much omega-6 fatty acids without enough omega-3s can potentially promote inflammation, which is linked to various health conditions.
Also, the source of your polyunsaturated fats matters. While whole foods like fish, nuts, and seeds are beneficial, many processed foods high in polyunsaturated fats also contain trans fats and added sugars. Consuming these foods regularly can lead to negative health outcomes, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Instead, you should focus on getting your polyunsaturated fats from wholesome, minimally processed foods.
- Potential weight gain if consumed in excess
- Can promote inflammation if equal balance isn’t met
- Heart disease
- Type 2 diabetes
Why avoid Polyunsaturated Fats?
There is no need to avoid polyunsaturated fats outright. These fats are a necessary part of the diet and offer numerous health benefits. However, it is important to balance polyunsaturated fat intake with other types of dietary fats and to monitor overall caloric intake. Overconsumption of any type of fat can lead to excessive caloric intake, which can result in weight gain and associated health issues.
More importantly, while polyunsaturated fats can be found in healthful foods like fish and nuts, they also appear in processed and fried foods. Such foods can contain harmful trans fats and be high in salt and sugar. You should focus on obtaining polyunsaturated fats from high-quality, unprocessed sources.
Are Polyunsaturated Fats higher in calories?
All fats, including polyunsaturated, monounsaturated, and saturated fats, provide the same amount of calories per gram. Specifically, each gram of fat supplies the body with 9 calories, making it the most calorie-dense nutrient. Consequently, while polyunsaturated fats offer several health benefits, they should be consumed mindfully to avoid excessive calorie intake.
It’s important to recognize that the type of fat you consume is as important as the quantity. Prioritize polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats over saturated and trans fats, while keeping your total fat intake within recommended levels.
Are polyunsaturated fats solid at room temperature
No, polyunsaturated fats are generally not solid at room temperature. The presence of multiple double bonds in their chemical structure affects their physical state, rendering them liquid even at moderate temperatures. This liquidity distinguishes polyunsaturated fats from saturated fats, which typically exhibit a solid form when kept at the same temperature like other forms of unsaturated fat.
It’s important to note that this physical characteristic of polyunsaturated fats can serve as a helpful guide when choosing cooking oils and other dietary fats. Foods and oils that remain liquid at room temperature tend to be higher in polyunsaturated fats, contributing to a healthier diet.
What is the difference between Polyunsaturated and Monounsaturated Fats?
Polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats are both types of unsaturated fats, deemed healthier than their saturated counterparts. The primary distinction lies in their chemical structure. Polyunsaturated fats have more than one double bond in their carbon chain, while monounsaturated fats have just one double bond.
These differences in structure influence how these fats function in your body. Both types can help reduce levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol, but polyunsaturated fats also include essential fats your body needs but can’t produce. While both types of fats should be included in a healthy diet, a balance between them is crucial to maximize health benefits.


